In the fast-paced world of automotive design, staying ahead means embracing innovation. Siemens Digital Industries Software is at the forefront of this transformation, revolutionizing vehicle development with their Virtual Prototype Assembly (VPA) technology. This cutting-edge approach to vehicle Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) performance prediction is reshaping how automotive engineers approach prototyping, offering significant cost savings and increased efficiency.
The Cost of Physical Prototypes
Traditionally, the automotive industry has relied heavily on physical prototypes to test and refine vehicle designs. However, these prototypes come with a hefty price tag, ranging from $250,000 to $1 million each. With development programs requiring up to 70 prototypes, the financial burden becomes substantial. Siemens proposes a shift from physical to virtual prototyping, leveraging hybrid test-CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) models to predict NVH performance early in the development process.
The Push for Virtual Prototyping
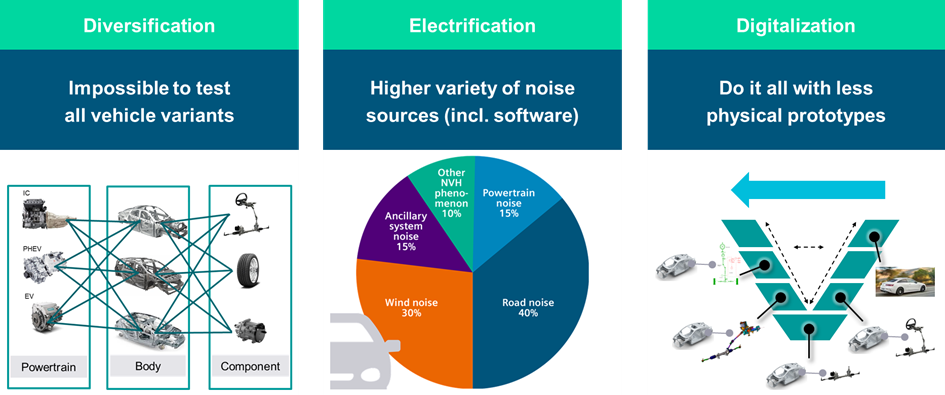
The automotive industry faces pressure from several trends: diversification, digitalization, and electrification. These trends demand more vehicle variants, fewer physical prototypes, and a greater variety of noise sources, respectively. Virtual prototyping offers a solution by assembling digital models that integrate test data and CAE components, reducing the need for physical testing.
Virtual Prototype Assembly: A Game Changer
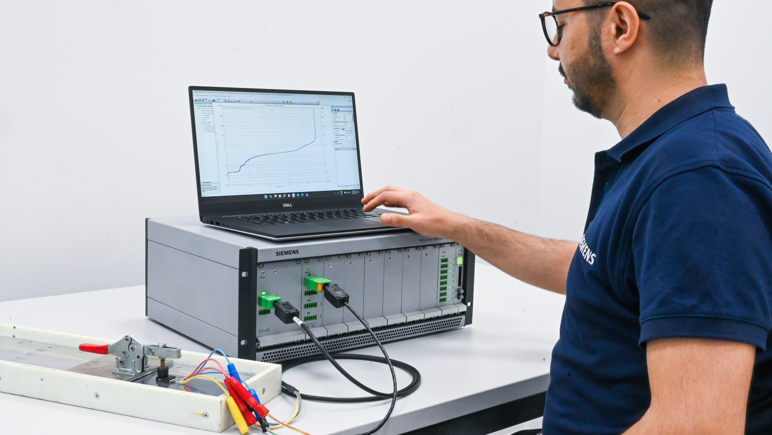
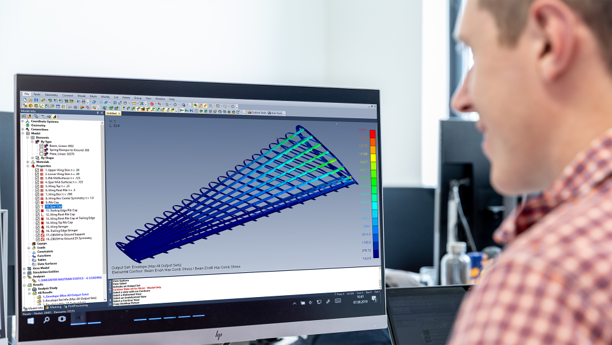
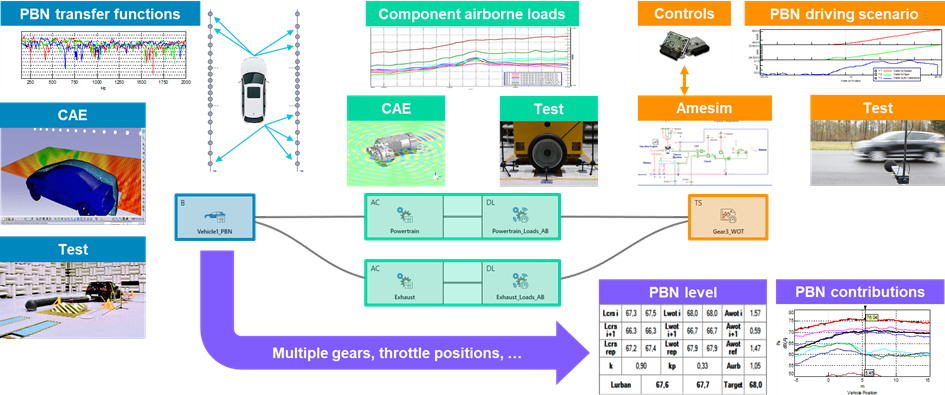
Siemens’ VPA technology enables engineers to replace physical prototypes with virtual assemblies. This approach utilizes Frequency-Based Substructuring (FBS) and Component-based Transfer Path Analysis (C-TPA) to predict road noise and other NVH attributes. By characterizing components like tires and suspensions separately and assembling them virtually, engineers can predict vehicle performance more accurately and efficiently.

Read more about Renault success here: https://resources.sw.siemens.com/en-US/case-study-renault-nvh/
Real-World Applications and Adoption
Major automotive players like Renault have already adopted VPA technology, expanding their NVH prediction applications fivefold and significantly reducing the reliance on physical prototypes. The process involves building a standardized component library, facilitating collaboration across different teams, and integrating with tools like Simcenter Testlab NVH Simulator for comprehensive analysis.
Benefits of Virtual Prototyping
The benefits of adopting virtual prototyping are clear. By eliminating physical prototypes, companies can save significant costs and resources. Additionally, virtual prototyping allows for early identification of potential issues, enabling engineers to make informed design decisions. The integration of virtual models with test data enhances accuracy, making the process reliable and scalable.
Conclusion
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, embracing virtual prototyping becomes crucial for staying competitive. Siemens Digital Industries Software is leading the charge with their innovative VPA technology, offering a glimpse into a future where vehicle development is faster, more cost-effective, and technologically advanced. By bridging the gap between the physical and virtual worlds, Siemens is setting a new standard in automotive prototyping, paving the way for smarter and more sustainable vehicle design.
For more information on how Siemens is transforming automotive prototyping, visit their case studies on Hyundai and Renault, and explore the potential of virtual prototyping to revolutionize your vehicle development process.